Sliding Puzzle
Generating...
What is Sliding Puzzle?
Sliding Puzzle (also known as the "Sliding Tile Puzzle" or "15 Puzzle") is a classic intellectual game that challenges logical reasoning. Players need to move tiles within a fixed grid to arrange them in numerical order, ultimately creating a complete sequence from 1 to N. This game helps enhance logical thinking, spatial imagination, and concentration, making it suitable for players of all ages.
Supported Grid Modes:
- 3×3 (8-Puzzle) —— Suitable for beginners with simple rules
- 4×4 (Classic 15-Puzzle) —— Standard difficulty, widely popular
- 5×5 to 9×9 —— Advanced challenges, for high-level players
How to Play Sliding Puzzle?
Basic Rules
- Start the Game: Click the "New Game" button, and the system will randomly shuffle the tiles.
- Move the Tiles: Click a tile or use the keyboard arrow keys to move it into the empty space.
- Arrange the Order: The goal is to arrange the tiles in ascending order (1 → 2 → 3 → …), leaving one blank space in the bottom-right corner.
- Time Tracking: The game will automatically record your time and steps, allowing you to challenge yourself to achieve the best solution time!
Advanced Features
- Custom Difficulty: Choose from grids ranging from 3×3 to 9×9 to tackle more complex puzzles.
- Auto-Solve: Stuck on a puzzle? Click "Auto Solve" and let the AI show you the optimal solution to learn expert techniques. Or, try our Sliding Puzzle Solver to input any custom layout and watch it solve step-by-step — perfect for studying tricky scenarios.
Quick Tips for Solving Sliding Puzzle
To solve the puzzle quickly, using the right strategies is key! Unlike the traditional "solve row by row" method, the "row and column cross" strategy allows you to reduce the problem's size step-by-step, avoiding unnecessary moves and speeding up the solving process!
Step 1: Solve the First Row
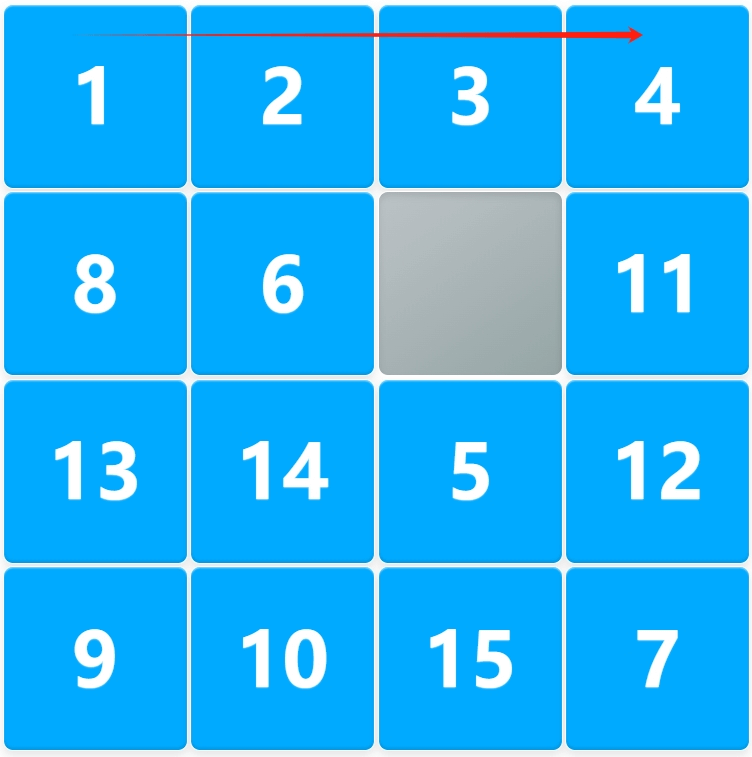
- Arrange the first row's numbers (1 → 2 → 3 → …) in order.
- Move the tiles while keeping the empty space near the target number so that the tiles naturally fall into place.
- Avoid disrupting the already arranged tiles.
Once the first row is fixed, it won't be disturbed anymore, reducing the puzzle size to an (N-1)×(N) puzzle.
Step 2: Solve the First Column
The first column is essentially an arithmetic sequence, where the values of each cell follow this formula:
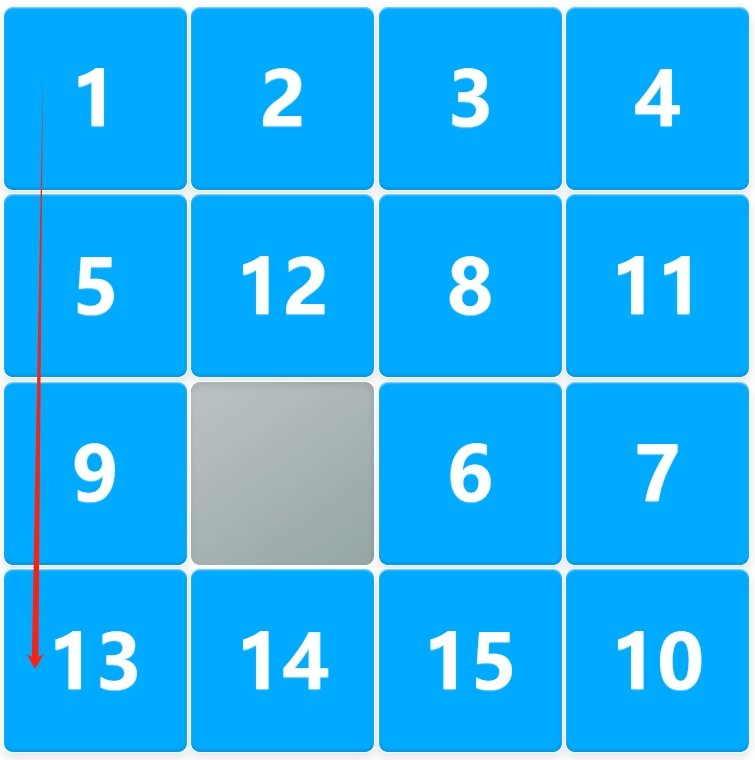
- For example, in a 4×4 puzzle, the first column should be arranged as:
- 1
- 5
- 9
- 13
- Move the tiles in order to restore the first column, without disturbing the first row.
Once these two steps are completed, the puzzle size reduces further to an (N-1)×(N-1) puzzle.
Step 3: Reduce the Puzzle and Continue with the Row and Column Cross Strategy
Now, the remaining part is a smaller puzzle (e.g., a 4×4 becomes a 3×3). Continue solving it with the row and column cross method:
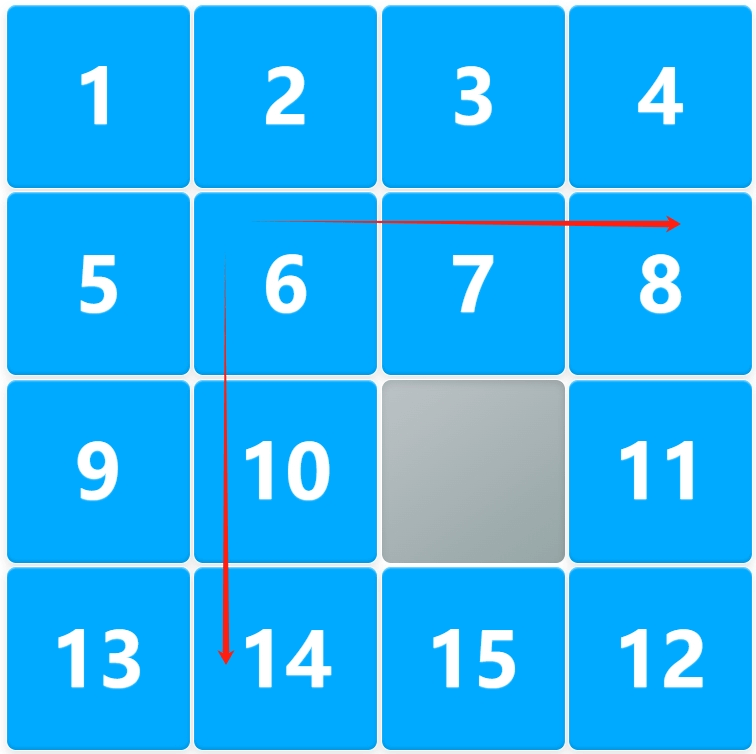
- First, solve the second row (ensure the correct order).
- Then solve the second column (keep the arithmetic sequence intact).
- Continue reducing the grid until you're left with the last 2×2 block.
This method minimizes steps and avoids unnecessary moves!
Step 4: Handle the Last 2×2 Tiles
When only two numbers remain to be swapped, don't just force them into place. Instead, use the "Z-rotation" strategy:
- Move the empty space so the two tiles swap positions.
- Ensure that the already arranged tiles do not get disturbed during this move.
Advanced Techniques
- Empty Space Control: Always keep the empty space near the target number so that the tiles naturally fall into place.
- Reverse Thinking (Backward Strategy): Instead of randomly moving tiles, first observe where the target number should be, and then figure out the path it needs to take. Move obstacles out of the way before adjusting the target number to avoid wasting moves.
- Practice and Learn from Experts: Use the AI's "Auto Solve" feature to learn optimal movement paths. Practice on different grid sizes, from 3×3 to 9×9, and get comfortable with the row and column cross method.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Why can't some Sliding Puzzles be solved?
In even-numbered puzzles (like 4×4 or 6×6), if the initial configuration cannot be restored to the correct order with an even number of swaps, the puzzle is unsolvable. However, this game only generates solvable puzzles, ensuring every game is winnable.
-
What is the optimal number of moves for Sliding Puzzle?
The optimal solution depends on the initial configuration, but typically:
- 3×3 (8-Puzzle): Optimal solution ≈ at least 31 moves
- 4×4 (15-Puzzle): Optimal solution ≈ at least 80 moves
- The difficulty increases exponentially with larger grids, but mastering techniques can help reduce the number of moves.
-
How to challenge higher difficulty?
- Increase the grid size, from 3×3 to gradually tackle 9×9.
- Try a step limit challenge to see if you can complete the puzzle with the fewest moves possible.