Futoshiki
What is Futoshiki?
Futoshiki is a challenging logic puzzle game originating from Japan, also referred to as "Inequality Sudoku." The rules are similar to traditional Sudoku, but the game introduces inequality symbols like "greater than (>)" and "less than (<)" between adjacent cells, adding a whole new layer of complexity to the puzzle-solving process!
Game Rules:
- Numbers cannot repeat in any row or column.
- Inequality symbols (either > or <) constrain the relationships between adjacent cells.
- The goal is to fill the grid according to the rules, ensuring that all inequalities are satisfied.
How to Play Futoshiki?
- Choose the grid size (3×3, 4×4, … 9×9); the larger the grid, the higher the difficulty.
- Select the difficulty level (Easy / Medium / Hard), which determines how many numbers and inequalities are provided initially.
- Use the given numbers and inequalities to infer the correct numbers for the blank cells.
- The system automatically detects errors, and any incorrect entries will be highlighted for you.
- Complete the puzzle by filling in all the numbers while satisfying all the rules to win!
Helpful Features
- "Answer" button: View the full solution for the current puzzle. Need help with a custom puzzle? Try our Futoshiki Solver to instantly check if it’s solvable and reveal the correct answer.
- "Reset" button: Return to the initial state and try the puzzle again.
How to Solve Futoshiki Faster?
1. Start with the inequalities and find the maximum or minimum values
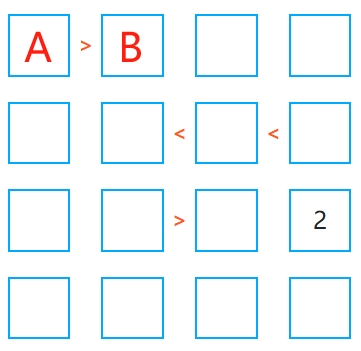
When you see A > B, A cannot be the smallest number, and B cannot be the largest number. For example, in a 4×4 grid where the numbers range from 1-4, if A > B, then B cannot be 4, and A cannot be 1.
2. Fill in the "only possible" numbers first
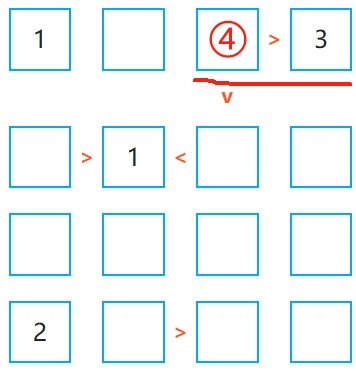
If a row or column has only one empty cell left, its value is determined and can be filled directly. If a cell only fits one number according to the inequality, that is its only solution.
3. Use row and column elimination to reduce possible candidates
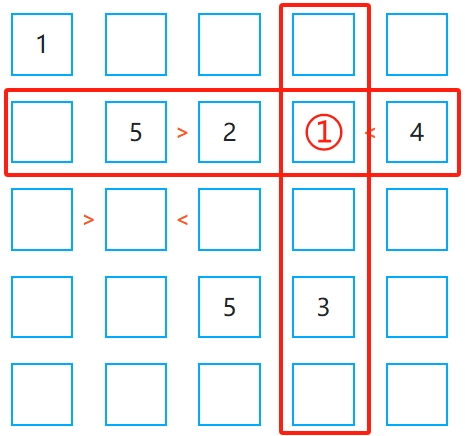
Since numbers cannot repeat in any row or column, you can use elimination to narrow down potential values. For example, in a 5×5 grid, if a row already contains 1, 2, 4, and 5, the remaining empty cell can only be filled with 3.
4. Look for inequality chains and deduce number ranges
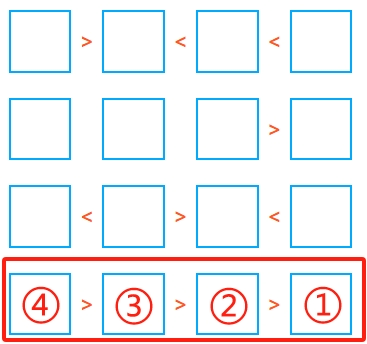
If you encounter a chain like A > B > C > D, you can immediately deduce their possible values. For example, in a 4×4 grid, if A > B > C > D, then A must be 4, B must be 3, C must be 2, and D must be 1.
5. Use "backtracking" for complex cases
Try filling in a possible number and continue deducing. If you encounter a contradiction, backtrack to the previous step and try a different number.
Common Questions
-
Futoshiki What's the difference between Futoshiki and Sudoku?
Traditional Sudoku only requires "no repetition in rows and columns," whereas Futoshiki adds inequality constraints between adjacent cells, increasing the difficulty of the puzzle-solving process.
-
Why does a number have a red background?
This indicates an error in the number entered. Possible mistakes include:
- The number is repeated in the same row or column.
- The number doesn't satisfy the ">" or "<" inequality relationship.
-
How can I solve the puzzle faster?
Start with the inequalities, combine uniqueness, elimination, and logical reasoning to gradually narrow down the possible numbers.
-
What's the difference between Easy, Medium, and Hard difficulty levels?
The difficulty level affects the number of initial clues given. In Easy mode, there are more pre-filled numbers and fewer inequalities. In Hard mode, fewer clues are provided, and there are more inequality constraints to work with.